[Codevel Project] – Search Bar and Pagination
I. Overview
If you’ve browsed through this site, you may have noticed that some pages include a search bar — it’s designed to help users search and sort posts, code samples, or other content.
Additionally, pagination is used to prevent overloading the page by fetching too much data at once.
This article mainly focuses on how to handle UI interactions involving the Search Bar (including the search input and sort buttons) and the Pagination Buttons.
II. Search Bar Structure
On the Codevel.io posts page, the search bar is divided into two main parts:
-
Sort Button: Allows sorting by
latest,read, orliked. -
Search Input: Captures the user’s input via the
onChangeevent.
When I previously worked with Angular, I handled this kind of feature by listening for onClick or onKeyUp/onKeyDown events, then calling an API to update the component.
That workflow looked like this:
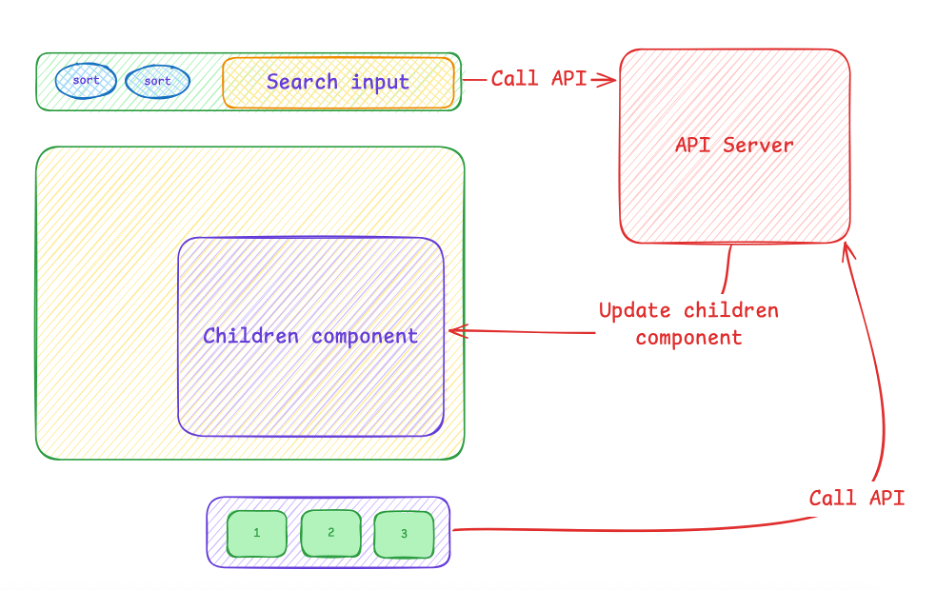
This approach updates only the necessary child components — which is efficient since the browser doesn’t need to reload the whole page.
However, it also creates an annoying issue:
If the user navigates from page 1 → page 2, and then clicks Back, the browser won’t restore the original page state (e.g., page number, search term, sort option). Instead, it reloads the previous route.
This becomes frustrating when there are dozens or hundreds of pages — users can’t easily return to their previous browsing state.
III. Switching to Next.js
When I switched to Next.js, I decided to move page, sort, and search data into URL query parameters.
For example:
https://codevel.io/posts?page=1&sort=liked&search=codevelNow, whenever the user interacts with any search-related component, the URL updates accordingly.
This allows server-side data fetching based on the current query parameters.
So if a user changes page=2 and later clicks Back, the page correctly returns to page=1 — maintaining the intended state.
IV. Implementation: Search Bar Component
'use client';
import { usePathname, useRouter, useSearchParams } from "next/navigation";
import { useDebouncedCallback } from "use-debounce";
import clsx from "clsx";
function SearchBar(props: { placeholder: string; showSort: boolean }) {
const searchParams = useSearchParams();
const pathname = usePathname();
const { replace } = useRouter();
const handleSearch = useDebouncedCallback((term) => {
const params = new URLSearchParams(searchParams);
params.set("page", "1");
params.set("sort", "latest");
if (term) {
params.set("search", term);
} else {
params.delete("search");
}
replace(`${pathname}?${params.toString()}`);
}, 300);
function handleSort(term: string) {
const params = new URLSearchParams(searchParams);
params.set("sort", term || "latest");
replace(`${pathname}?${params.toString()}`);
}
return (
<div className="search-line border-bottom pb-1">
<div className={clsx("card card-group-button", { "d-none": !props.showSort })}>
<div className="card-body d-flex p-1">
<button onClick={() => handleSort("latest")} className={searchParams.get("sort") === "latest" ? "btn btn-sort active" : "btn btn-sort"}>Latest</button>
<button onClick={() => handleSort("read")} className={searchParams.get("sort") === "read" ? "btn btn-sort active" : "btn btn-sort"}>Read</button>
<button onClick={() => handleSort("liked")} className={searchParams.get("sort") === "liked" ? "btn btn-sort active" : "btn btn-sort"}>Liked</button>
</div>
</div>
<div className="search-bar">
<div className="border form-icon">
<button className="btn px-0" type="submit">
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="18" height="18" fill="currentColor" className="bi bi-search ms-2" viewBox="0 0 16 16">
<path d="M11.742 10.344a6.5 6.5 0 1 0-1.397 1.398l3.85 3.85a1 1 0 0 0 1.415-1.414z"/>
</svg>
</button>
<input
type="text"
placeholder={props.placeholder}
className="flex-fill form-control form-control-sm"
onChange={(e) => handleSearch(e.target.value)}
defaultValue={searchParams.get("search")?.toString()}
/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
export default SearchBar;
Key Concepts Explained
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| useSearchParams() | Returns URL query parameters (search, sort, page, …). |
| usePathname() | Returns the current relative path (without query params). |
| useRouter() | Hook that allows client-side URL navigation. |
| useDebouncedCallback() |
Prevents excessive API calls — triggers only after 300 ms of no typing. |
Behavior
-
When the user types in the search input, the page resets to
page=1andsort=latest. -
If the input is cleared, the
searchparameter is removed from the URL. -
Sorting buttons (
latest,read,liked) update thesortquery param directly.
V. Pagination Component
Pagination helps limit the amount of data displayed per page, improving performance and user experience.
'use client';
import { usePathname, useSearchParams } from "next/navigation";
import clsx from "clsx";
import Link from "next/link";
function Pagination({ totalPages }: { totalPages: number }) {
const pathname = usePathname();
const searchParams = useSearchParams();
const currentPage = Number(searchParams.get("page")) || 1;
const createPageURL = (pageNumber: number | string) => {
const params = new URLSearchParams(searchParams);
params.set("page", pageNumber.toString());
return `${pathname}?${params.toString()}`;
};
return (
<div className={clsx("mt-3", { "d-none": totalPages <= 1 })}>
<nav className="d-flex justify-content-end">
<ul className="pagination pagination-sm">
<li className={clsx("page-item", { disabled: currentPage === 1 })}>
<Link className="page-link me-1" href={createPageURL(1)}>1</Link>
</li>
<li className={clsx("me-1 d-none align-items-center", { "d-flex": currentPage > 3 })}>…</li>
<li className={clsx("me-1 d-none align-items-center", { "d-flex": currentPage < totalPages - 2 })}>…</li>
<li className={clsx("page-item", { disabled: currentPage === totalPages })}>
<Link className="page-link" href={createPageURL(totalPages)}>{totalPages}</Link>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
</div>
);
}
export default Pagination;
How It Works
-
Shares similar logic with the Search/Sort functions.
-
Each pagination button triggers a URL update (
?page=). -
When the query param changes, the component re-renders with updated server-side data.
Demo Interface
VI. Summary & Next Post
In this article, we explored how to implement a search bar and pagination system using Next.js hooks such as useRouter(), useSearchParams(), and usePathname().
We also saw how to debounce input handling and synchronize search, sort, and pagination through URL query parameters.
In the next post, I’ll demonstrate how to create a Client Component that calls APIs directly whenever users interact with the interface — for example, triggering real-time data updates when typing or changing filters.

