[Codevel Project] – Access With JWT Token
I. Introduction
JWT (JSON Web Token) is an encoding standard that lets developers safely exchange data between client and server.
Every request includes the token in the header:
Authorization: Bearer <JWT Token>
II. JWT in Codevel.io
In Codevel.io, or any REST-based web application with authentication and authorization, I rely on JWT.
A JWT token typically includes at least four key claims:
-
usernameorid: identifies the user. -
role: defines user permission (ROLE_USER, ROLE_ADMIN, etc.). -
iat(Issued At): when the token was issued. -
exp(Expiration): when the token expires.
{
"username": "codevel",
"role": "ROLE_ADMIN",
"iat": 1761406843,
"exp": 1761766843
}
III. JWT Workflow
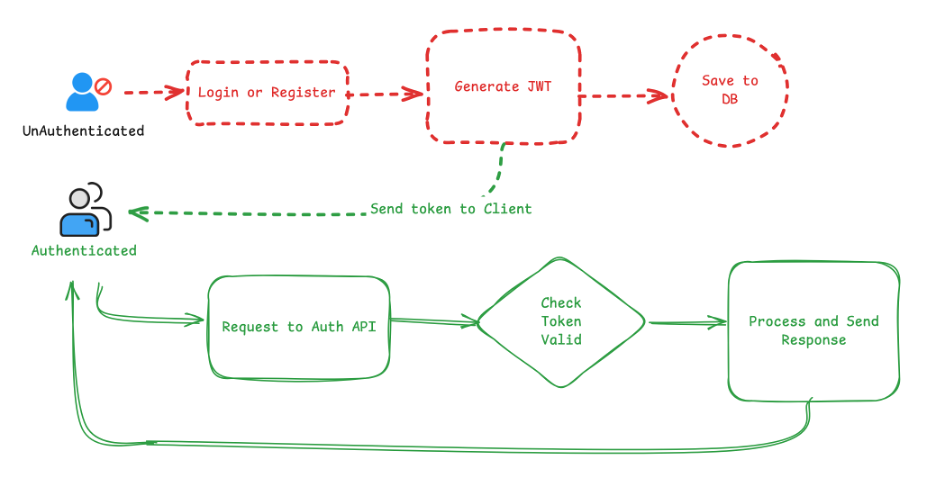
The workflow is straightforward:
-
The user logs in or registers successfully.
-
The server generates a JWT token.
-
The token is stored in the database for validation.
-
The client saves it (cookie or local storage).
-
Each request includes the token in the
Authorizationheader.
IV. Backend (Spring Boot)
Generate & validate JWT tokens.
1. Generate Token
public TokenResponse generateToken(String username, String role) {
String jwt = Jwts.builder()
.claim("username", username)
.claim("role", role)
.issuedAt(new Date())
.expiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + jwtExpirationMs))
.signWith(key)
.compact();
TokenEntity tokenEntity = new TokenEntity();
tokenEntity.setToken(jwt);
tokenEntity.setUsername(username);
tokenRepository.save(tokenEntity);
return new TokenResponse(jwt, username,
new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + jwtExpirationMs), role);
}
I also store it in the DB to prevent forged tokens from being accepted.
2. Extract Token
public String getTokenFromHeader(HttpHeaders headers) {
String token = headers.getFirst("Authorization");
if (Objects.isNull(token) || token.isEmpty()) return null;
if (token.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
return token.substring(7);
}
return null;
}
3. Validate Token
public boolean validateToken(String token) {
TokenEntity tokenEntity = tokenRepository.findByToken(token);
if (Objects.isNull(tokenEntity)) return false;
try {
Jwts.parser()
.verifyWith(key)
.build()
.parseSignedClaims(token);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
return false;
}
}
parseSignedClaims() will check the expiration (exp) itself and throw ExpiredJwtException if the token has expired.
4. Extract Username
public String getUsername(String token) {
if (Objects.isNull(token) || !validateToken(token)) return null;
return Jwts.parser()
.verifyWith(key)
.build()
.parseSignedClaims(token)
.getPayload()
.get("username").toString();
}
V. Frontend (Next.js)
On the client side, after a successful login, the server returns a JWT.
Next.js saves it in cookies using the cookies() API from next/headers.
1. Login & Save Session
export async function login(initialState: any, formData: FormData) {
const jsonData = Object.fromEntries(formData.entries());
const res = await fetch(process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_USER_API_URL + '/login', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify(jsonData),
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
cache: "no-store",
});
if (!res.ok) return { message: "Username or password is incorrect." };
const response = await res.json();
const cookieStore = await cookies();
cookieStore.set('session', JSON.stringify(response));
revalidatePath("/", "layout");
redirect(initialState?.next || '/');
}
2. Attach JWT in Requests
export async function getHeaders(required: boolean = true, pathname: string = "") {
const cookieStore = await cookies();
const token = cookieStore.get("session")?.value || "{}";
const expires = JSON.parse(token).expires;
if (required && (token == "{}" || expires < Date.now())) {
redirect("/login?next=" + pathname);
}
return token == "{}"
? { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', Authorization: '' }
: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${JSON.parse(token).token}`,
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
};
}
3. Eg. Fetch User Info
export async function getInfo(): Promise<UserResponse | null> {
const headers = await getHeaders();
const res = await fetch(process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_USER_API_URL + '/auth/info', {
headers: headers
});
return res.json() as Promise<UserResponse>;
}
VI. Remove Token
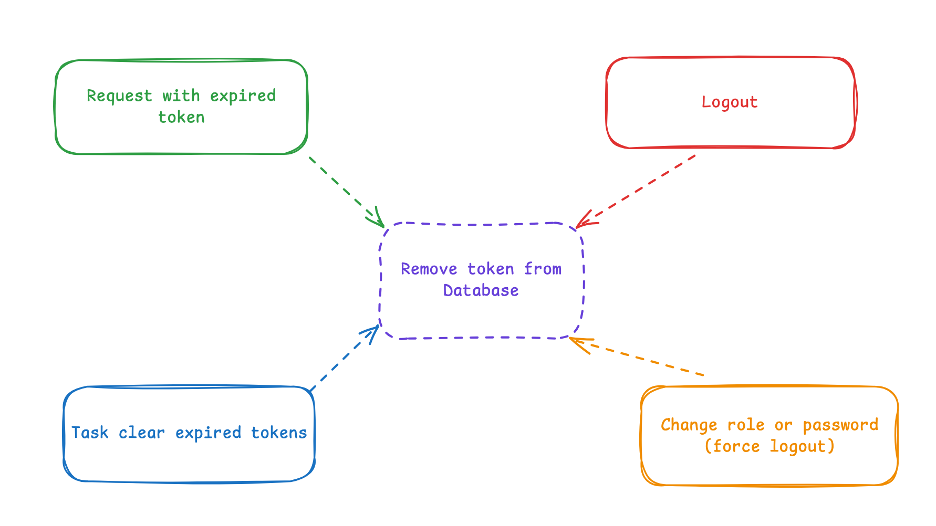
You should remove or invalidate tokens when:
-
Token expired (
exp<Date.now()). -
User logs out.
-
Routine cleanup of expired tokens.
-
User’s role or password changed → force logout.
VII. Summary
JWT provides a simple and powerful authentication mechanism.
Combined with controlled storage (e.g., token DB) and SecurityFilterChain, it ensures both security and scalability.

